CBSE 12TH MATHEMATICS - Online Test
Q1. t dt is equal to
Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
=[sint]π/2−π/2=sinπ2−sin(−π2)=1+1=2
Q2. Position vectors of points A, B, C, etc., with respect to the origin O are generally denoted by
Answer : Option B
Explaination / Solution:
Position vectors of any point in space are usually calculated from the origin, so we write three points A ,B,C in space to represent the origin as the initial point.
Q3. A coin is tossed three times, E : at most two tails , F : at least one tail. Find P(E|F)
Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
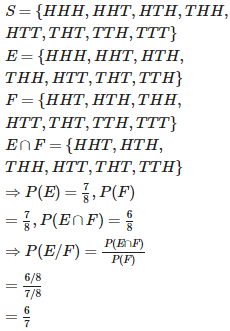
Q4. The maximum value of sin x + cos x is
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
(12√)+(12√)=2–√
Q5. is equal to
Answer : Option B
Explaination / Solution:
Q6. Degree of a differential equation, when the equation is polynomial equation in y′ is
Answer : Option B
Explaination / Solution:
The power or index of the highest ordered derivative in the polynomial is the degree of the differential equation provided equation is in the standard form.
Q7.
is a vector joining two points P(x1, y1, z1) and Q(x2, y2, z2).If ,Direction cosines of are
Answer : Option A
Explaination / Solution:
since we know Direction cosines of a line are coefficient of i,j,k of a unit vector along that line,first find a vector then to convert it unit vector divide by its magnitute || the coefficient of this unit vector will be
Q8. The area enclosed between the curves y = ,x- axis and two ordinates x = 1 to x = 2 is [ in square units ]
Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
Required area :
= = = = == sq units
Q9. is the matrix
Answer : Option B
Explaination / Solution:
It is an identity matrix with the order 2*2,
Q10. Let f be a real valued function defined on (0, 1) ∪(2, 4) such that f ‘ (x) = 0 for every x, then
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
f ‘ (x) =0 f (x) is constant in ( 0 , 1 ) and also in ( 2, 4 ). But this does not mean that f ( x) has the same value in both the intervals . However , if f ( c ) =f ( d ) , where c ( 0 , 1 ) and d ( 2, 4) then f ( x ) assumes the same value at all x ( 0 ,1 ) U (2, 4 ) and hence f is a constant function.
