Hydrocarbons - Online Test
Q1. Carbon-carbon double bond in alkenes consists of
Answer : Option A
Explaination / Solution:
sigma bond is formed by head-on overlap of sp2 hybridised orbitals while the pi bond is formed by lateral or sideways overlapping of the two 2p-orbitals of the two carbon atoms. Alkenes contain 1 weak pi bond and 1 strong sigma bond.
Q2. In the alkene having IUPAC name 3-Methyl-1-butene the double bond lies on carbon atom numbered
Answer : Option B
Explaination / Solution:
‘1’ is written before butene which indicates that the position of the double bond is on carbon 1.The structure of the compound is: CH2=CHCH(CH3)CH3
Q3. Stereoisomeric alkenes due to different arrangement of atoms or groups in space are referred to as
Answer : Option A
Explaination / Solution:
Isomers which have the same structural formulae but difffer in the relative spatial arrangements of atoms or groups around the double bond are called geometric isomers.athus geometrical isomers are atype of stereoisomers.
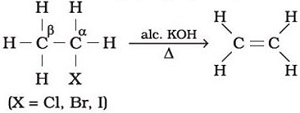
Q4.
One of the methods of preparing ethylene is given below.This is an example of _______ reaction
Answer : Option B
Explaination / Solution:
Dehydration of alcohols in the presence of alc. KOH to form an alkene is an example of elimination reaction.
Q5. The boiling point of isomeric branched chain alkene is
Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
As surface area decreases with branching,the boiling point also decreases.
Q6. The reaction given below is used to produce polythene. This is an example of _______ reaction


Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
In polymerisation reaction many monomeric units combine to form a big macromolecule.
Q7. The number of position isomers of is
Answer : Option A
Explaination / Solution:
n-pentyne , 3-methyl butyne, pent-2-yne
Q8. Thus ethyne molecule consists of
Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
Ethyne is an unsaturated compound which belongs to the alkyne family and has the formula C2H2.Thus it consists of one C–C σ bond, two C–H σ bonds and two C–C π bonds.
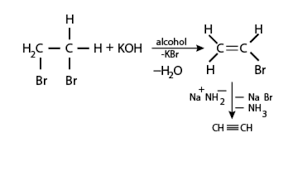
Q9. The preparation of alkynes from vicinal dihalides is an example of---------- ?
Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
Elimination reaction is a type of organic reaction in which two substituents are removed from a molecule in either one or two steps .When the starting dihalide is a vicinal dihalide , alkyne is obtained by two successive elimination reactions.
Example :
Vicinal dihalide, on treatment with forms a monosubstituted alkene Vinyl bromidewhich when reacted with sodium amide , forms ethyne (ie. an alkyne ). The steps of conversion are ,
Q10. Majority of the reactions of alkynes are the examples of
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
Alkynes have two pi bonds,hence they are electron rich species.They attract electrophiles thereby undergoing electrophilic addition reactions.