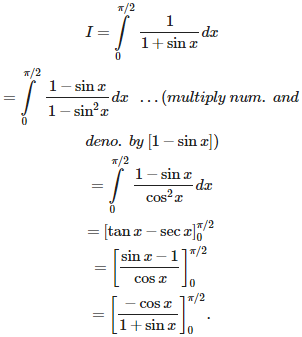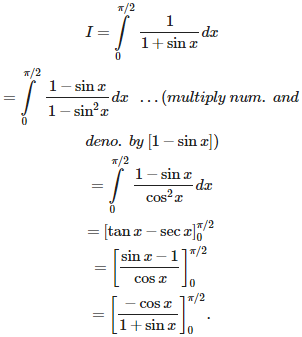CBSE 12TH MATHEMATICS - Online Test
Q1. If [x] stands for the integral part of x, then
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
The is defined as the value which takes the nearest small integer in every integer interval . For example in the interval the value of the function is 0 since it is the lowest integer in that interval . Hence which gives the value as 1,which is the lowest integer of that interval.
Q2. The order of the equation = 0 is
Answer : Option B
Explaination / Solution:
Since the highest derivative term is hence the order is 3.
Q3. If l, m, n are the direction cosines and a, b, c are the direction ratios of a line then
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
using direction ratio a,b,c we got a vector along the line ,for direction cosine find unit vector then  where l,m,n represent direction cosine
where l,m,n represent direction cosine
 where l,m,n represent direction cosine
where l,m,n represent direction cosine
Q4. AOB is the positive quadrant of the ellipse in which OA = a and OB = b . The area between the arc AB and chord AB of the ellipse is
Answer : Option B
Explaination / Solution:
Required area :
= area of ellipse – area of right angled triangle AOB.
= area of ellipse – area of right angled triangle AOB.
= ab – ab = ( - 2 ) .
Q5. The number of all the possible matrices of order 2 × 2 with each entry 0, 1 or 2 is
Answer : Option A
Explaination / Solution:
The number of elements in a 2 x 2 matrix is the product 2 x 2 =4
Each element can either be a 0,1 or 2.
Given this, the total possible matrices that can be selected is 34
Q6. The function f (x) = 2 – 3 x is
Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
f (x) = 2 – 3x f ‘ (x) = - 3 < 0 for all x R . so, f is strictly decreasing function.
Q7. If A and B are square matrices of order 3 , then
Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
If A B be two square matrices of order 3 and if |B|=0, AB=0 then this is possible only if |A| may be zero
Q8. In linear programming, optimal solution
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
In linear programming, any point in the feasible region which gives that gives the optimal value (maximum or minimum) of the objective function is called optimal solution. In other words, it satisfies all the constraints as well as the objective function .
Q9. Which of the following is not an equivalence relation on I, the set of integers ; x, y
Answer : Option B
Explaination / Solution:
f R is a relation defined by xRy:ifx⩽y, then R is reflexive and transitive .But , it is not symmetric. Hence , R is not an equivalence relation.
Q10. is equal to
Answer : Option B
Explaination / Solution: