Communication Engineering - Online Test
Q1. 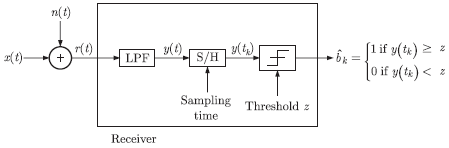
Consider a baseband binary PAM receiver shown below. The additive channel noise n(t) is with power spectral density 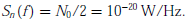 The lowpass filter is ideal with unity gain and cut-off frequency 1 MHz. Let Yk represent the random variable y(tk).
The lowpass filter is ideal with unity gain and cut-off frequency 1 MHz. Let Yk represent the random variable y(tk).
 The lowpass filter is ideal with unity gain and cut-off frequency 1 MHz. Let Yk represent the random variable y(tk).
The lowpass filter is ideal with unity gain and cut-off frequency 1 MHz. Let Yk represent the random variable y(tk).Yk = Nk , if transmitted bit bk = 0
Yk = a + Nk if transmitted bit bk = 1
Where Nk represents the noise sample value. The noise sample has a probability density function, 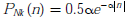 (This has mean zero and variance 2/α2). Assume transmitted bits to be equiprobable and threshold z is set to a/2
= 10-6 V.
(This has mean zero and variance 2/α2). Assume transmitted bits to be equiprobable and threshold z is set to a/2
= 10-6 V.
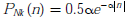 (This has mean zero and variance 2/α2). Assume transmitted bits to be equiprobable and threshold z is set to a/2
= 10-6 V.
(This has mean zero and variance 2/α2). Assume transmitted bits to be equiprobable and threshold z is set to a/2
= 10-6 V.
The value of the parameter α
(in V-1) is
Answer : Option B
Explaination / Solution:
Let response of LPF filters
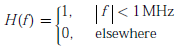
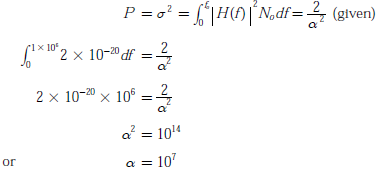
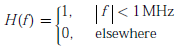
Noise variance (power) is given as
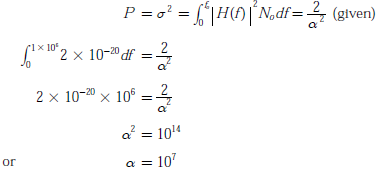
Q2. A Linear Time Invariant system with an impulse response h(t) produces output y(t)
when input x(t) is applied. When the input x (t−τ) is applied to a system with impulse
response h(t − τ), the output will be
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
No Explaination.
Q3. 
Consider a baseband binary PAM receiver shown below. The additive channel noise n(t) is with power spectral density 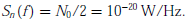 The lowpass filter is ideal with unity gain and cut-off frequency 1 MHz. Let Yk represent the random variable y(tk).
The lowpass filter is ideal with unity gain and cut-off frequency 1 MHz. Let Yk represent the random variable y(tk).
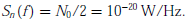 The lowpass filter is ideal with unity gain and cut-off frequency 1 MHz. Let Yk represent the random variable y(tk).
The lowpass filter is ideal with unity gain and cut-off frequency 1 MHz. Let Yk represent the random variable y(tk).Yk = Nk , if transmitted bit bk = 0
Yk = a + Nk if transmitted bit bk = 1
Where Nk represents the noise sample value. The noise sample has a probability density function, 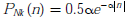 (This has mean zero and variance 2/α2). Assume transmitted bits to be equiprobable and threshold z is set to a/2 = 10-6 V.
(This has mean zero and variance 2/α2). Assume transmitted bits to be equiprobable and threshold z is set to a/2 = 10-6 V.
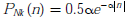 (This has mean zero and variance 2/α2). Assume transmitted bits to be equiprobable and threshold z is set to a/2 = 10-6 V.
(This has mean zero and variance 2/α2). Assume transmitted bits to be equiprobable and threshold z is set to a/2 = 10-6 V.
The probability of bit error is
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
Probability of error is given by
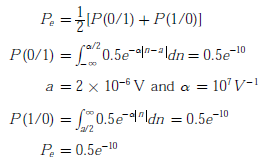
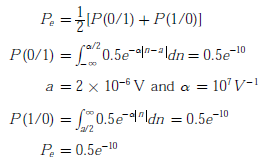
Q4. In a digital communication system, the overall pulse shape p(t) at the receiver before the sampler has the Fourier transform P(f). If the symbols are transmitted at the rate of 2000 symbols per second, for which of the following cases is inter symbol interference zero?
Answer : Option B
Explaination / Solution:
For ISI free pulse,
If P(t) is having spectrum P(f)
Then 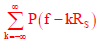 = constant
= constant
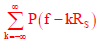 = constant
= constantRs = 2KSpa
Thin condition is met by pulse given in option B.
Q5. If the Laplace transform of a signal 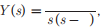 then its final value is
then its final value is
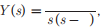 then its final value is
then its final value is
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
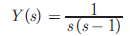
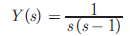
Final value theorem is applicable only when all poles of system lies in left half of S -plane. Here s = 1 is right s −plane pole. Thus it is unbounded.
Q6. Which one of the following statements about differential pulse code modulation (DPCM) is true?
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
DPCM Block diagram
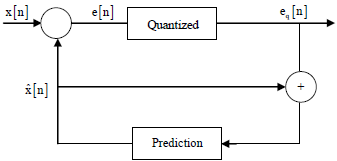

eq[n] is quantized e[n]
e[n] is difference of message signal sample with its prediction.
Q7. Three functions f(t), f2(t) and f3(t) which are zero outside the interval [0, T] are
shown in the figure. Which of the following statements is correct?
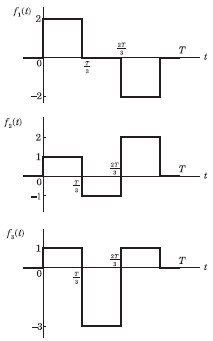

Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
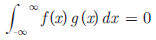
For two orthogonal signal f (x) and g(x)
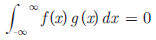
i.e. common area between f x and g x is zero.
Q8. The 3-dB bandwidth of the low-pass signal e-t u(t), where u(t) is the unit step
function, is given by
Answer : Option A
Explaination / Solution:
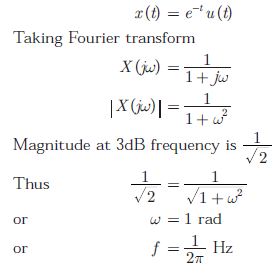

Q9. Consider a wireless communication link between a transmitter and a receiver located in free space, with finite and strictly positive capacity. If the effective areas of the transmitter and the receiver antennas, and the distance between them are all doubled, and everything else remains unchanged, the maximum capacity of the wireless link
Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
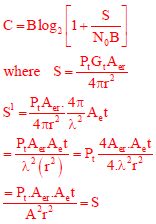
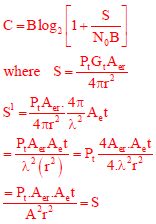
Channelcpacity remain same.
Q10. A Hilbert transformer is a
Answer : Option A
Explaination / Solution:
No Explaination.
