Programming and Data Structures - Online Test
Q1. Recall that Belady’s anomaly is that the pages-fault rate may increase as the number of
allocated frames increases. Now consider the following statements:
S1: Random page replacement algorithm (where a page chosen at random is replaced)
suffers from Belady’s anomaly
S2: LRU page replacement algorithm suffers from Belady’s anomaly
Which of the following is CORRECT ?
Answer : Option B
Explaination / Solution:
Statement 1 is “TRUE”. Because there can be a case when page selected to be replaced is by
FIFO policy.
Statement 2 is “FALSE”. Because LRU page replacement algorithm does not suffers
from Belady’s Anomaly. Only FIFO page replacement algorithm suffers from Belady’s
Anomaly.
Q2. Let G = (V, E) be any connected undirected edge-weighted graph. The weights of the edges in
E are positive and distinct. Consider the following statements:
(I) Minimum spanning tree of G is always unique.
(II) Shortest path between any two vertices of G is always unique.
Which of the above statements is/are necessarily true?
Answer : Option A
Explaination / Solution:
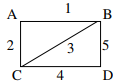

Shortest path from B to C are two B-A-C and B-C both of weight '3'
Q3. Which data structure in a compiler is used for managing information about
variables and their attributes?
Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
No Explaination.
Q4. Which languages necessarily need heap allocation in the runtime environment?
Answer : Option A
Explaination / Solution:
No Explaination.
Q5. Consider a B+ -tree in which the maximum number of keys in a node is 5. What is
the minimum number of keys in any non-root node?
Answer : Option A
Explaination / Solution:
No Explaination.
Q6. The cyclomatic complexity of each of the modules A and B shown below is
10. What is the cyclomatic complexity of the sequential integration shown on
the right hand side?
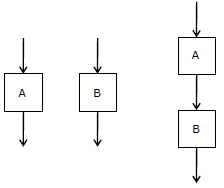

Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
No Explaination.
Q7. A system uses FIFO policy for page replacement. It has 4 page frames with no
pages loaded to begin with. The system first accesses 100 distinct pages in some
order and then accesses the same 100 pages but now in the reverse order. How
many page faults will occur?
Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
No Explaination.
Q8. The degree sequence of a simple graph is the sequence of the degrees of the nodes in the graph in decreasing order. Which of the following sequences can not be the degree sequence of any graph? I. 7, 6, 5, 4, 4, 3, 2, 1 II. 6, 6, 6, 6, 3, 3, 2, 2
III. 7, 6, 6, 4, 4, 3, 2, 2 IV. 8, 7, 7, 6, 4, 2, 1, 1
Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
No Explaination.
Q9. The following C function takes a simply-linked list as input argument. It modifies
the list by moving the last element to the front of the list and returns the
modified list. Some part of the code is left blank.
typedef struct node {
int value;
struct node *next;
} Node;
Node *move_to_front(Node *head) {
Node *p, *q;
if ((head = = NULL: || (head->next = = NULL)) return head;
q = NULL; p = head;
while (p-> next !=NULL) {
q=P;
p=p->next;
}
_______________________________
return head;
}
Choose the correct alternative to replace the blank line.
Answer : Option A
Explaination / Solution:
No Explaination.
Q10. The following program is to be tested for statement coverage:
begin
if (a = = b) {S1; exit;}
else if (c = = d) {S2;}
else {S3; exit;}
S4;
end
The test cases T1, T2, T3 and T4 given below are expressed in terms of the
properties satisfied by the values of variables a, b, c and d. The exact values are
not given.
T1 : a, b, c and d are all equal
T2 : a, b, c and d are all distinct
T3 : a=b and c !=d
T4 : a !=b and c=d
Which of the test suites given below ensures coverage of statements S1, S2, S3
and S4?
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
No Explaination.
