Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - Online Test
Q1. Bond angle helps us in
Answer : Option A
Explaination / Solution:
Bond angles also contribute to the shape of a molecule. Bond angles are the angles between adjacent lines representing bonds. The bond angle can help differentiate between linear, trigonal planar, tetraheral, trigonal-bipyramidal, and octahedral. The ideal bond angles are the angles that demonstrate the maximum angle where it would minimize repulsion, thus verifying the VSEPR theory.
Q2. The amount of energy required to break one mole of bonds of a particular type between two atoms in a gaseous state is called
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
Bond enthalpy, also known as bond energy, is the energy that is needed to break a particular bond in a gaseous compound. The unit that expresses bond enthalpy is kilojoules per mole, or kJ/mol.
Q3. H.O.H bond angle in water is
Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
Due to presence of two lone pairs on O in H2O bond angle reduce to 104.50 from 1090.
Q4. For , bond order is
Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
Bond order is the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms. in diatomic nitrogen N≡N, Triple covalent bond is present in nitrogen so the bond order is 3;
Q5. , CO and are isoelectronic molecules. Their respective bond order is :
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
Total number of electrons in N2 molecule is 7+ 7= 14.
As per the formula Bonded pair of electrons Nb:
Total 10 electrons.
Anti bond pairs of electrons Na: Total 4 electrons.
Bond Order (B.O.) =
Similarly bond order of CO And NO+ is 3
Q6. Structures of . ion given below explains the phenomenon of _____________.


Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
Resonance is the phenomenon when a molecule can be represented by 1 or more structure differing in the position of bonds and charge.
Q7. The product of the magnitude of the charge and the distance between the centres of positive and negative charge is called
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
A dipole moment is a measurement of the separation of two opposite electrical charges. Dipole moments are a vector quantity. The magnitude is equal to the charge multiplied by the distance between the charges and the direction is from negative charge to positive charge:
µ=q x r
Q8. the valence shell electron pair repulsion (vsepr) theory helps in the
Answer : Option A
Explaination / Solution:
Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory is a model used in chemistry to predict the geometry of individual molecules from the number of electron pairs surrounding their central atoms. It is also named the Gillespie-Nyholm theory after its two main developers.
Q9. In the formation of hydrogen molecule, overlapping of atomic orbitals which results in the pairing of electrons. These are:
Answer : Option A
Explaination / Solution:
overlapping of atomic orbitals having electrons of opposite spin take palce in the formation of molecule.
Q10. In NO-3 ion, the number of bond pairs and lone pairs of electrons on nitrogen atom are
Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
The nitrate ion is formed by the loss of the hydrogen ion, and so its structure is:
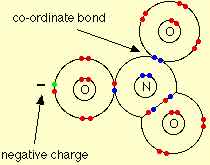
Around the central nitrogen there are 4 pairs of shared electrons, and no remaining lone pair. The original lone pair has now become a bonding pair. Two of those pairs make up a double bond. The double bond unit and the two single bonds arrange themselves as far apart as possible in a trigonal planar arrangement - exactly the same as the carbonate ion.
