Arithmetic - Online Test
Q1. A vehicle negotiates a transition curve with uniform speed v . If the radius of the
horizontal curve and the allowable jerk are R and J , respectively, the minimum
length of the transition curve is
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
No Explaination.
Q2. The value of one U.S. dollar is 65 Indian Rupees today, compared to 60 last year. The Indian
Rupee has ____________.
Answer : Option B
Explaination / Solution:
No Explaination.
Q3. In which of the following options will the expression P < M be definitely true?
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
No Explaination.
Q4. Find the next term in the sequence: 7G, 11K, 13M, ___
Answer : Option B
Explaination / Solution:
No Explaination.
Q5. The multi-level hierarchical pie chart shows the population of animals in a reserve forest. The
correct conclusions from this information are:
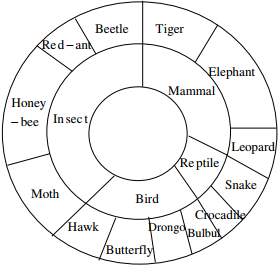

(i) Butterflies are birds
(ii) There are more tigers in this forest than red ants
(iii) All reptiles in this forest are either snakes or crocodiles
(iv) Elephants are the largest mammals in this forest
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
It is not mentioned that elephant is the largest animal
Q6. Customers arrive at a ticket counter at a rate of 50 per hour and tickets are issued in the order of their arrival. The average time taken for issuing a ticket is 1min. Assuming that customer arrivals form a Poisson process and service times are exponentially distributed, the average waiting time in queue in minutes is:
Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
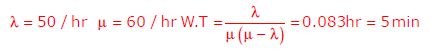
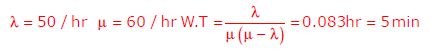
Q7. Cars arrive at a service station according to Poisson’s distribution with a mean
rate of 5 per hour. The service time per car is exponential with a mean of
10minutes. At steady state, the average waiting time in the queue is
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
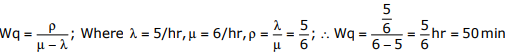
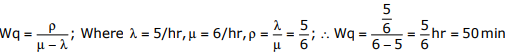
Q8. One unit of product P1 requires 3 kg of resource R1 and 1kg of resource R2 . One
unit of product P2 requires 2kg of resource R1and 2kg of resource R2. The profits
per unit by selling product P1 and P2 are Rs.2000 and Rs.3000 respectively. The
manufacturer has 90kg of resource R1 and 100kg of resource R2.
The unit worth of resource R2 i.e., dual price of resource R2 in Rs. Per kg is
Answer : Option A
Explaination / Solution:
Because the constraint on resource 2 has no effect on the feasible region.
Q9. One unit of product P1 requires 3 kg of resource R1 and 1kg of resource R2 . One unit of product P2 requires 2kg of resource R1and 2kg of resource R2. The profits per unit by selling product P1 and P2 are Rs.2000 and Rs.3000 respectively. The manufacturer has 90kg of resource R1 and 100kg of resource R2.
The manufacturer can make a maximum profit of Rs.
Answer : Option B
Explaination / Solution:
Optimum solution is: 0, 45 and maximum profit = Rs.135000
Q10. If Log (P) = (1/2)Log (Q) = (1/3) Log (R), then which of the following options is
TRUE?
Answer : Option B
Explaination / Solution:
No Explaination.
