REASONING - Online Test
Find the number of triangles in the given figure.

The figure may be labelled as shown.

The simplest triangles are BFG, CGH, EFM, FMG, GMN, GHN, HNI, LMK, MNK and KNJ i.e. 10 in number.
The triangles composed of three components each are FAK and HKD i.e. 2 in number.
The triangles composed of four components each are BEN, CMI, GLJ and FHK i.e. 4 in number.
The triangles composed of eight components each are BAJ and OLD i.e. 2 in number.
Thus, there are 10 + 2 + 4 + 2 = 18 triangles in the given figure.

Two person are not facing the centre - C & G
Find the number of triangles in the given figure.

The figure may be labelled as shown.

The simplest triangles are AEI, AIH, BEJ, BJF, CFK, CKG, DGL, DLH, EOJ, FOJ, FOG, LOG, HOL and HOE i.e. 14 in number.
The triangles composed of two components each are EAH, FBE, BEO, EOF, BFO, FCG, GDH, HOD, HOG and GOD i.e. 10 in number.
The triangles composed of three components each are EFH, EHG, FGH and EFG i.e. 4 in number.
Thus, there are 14 + 10 + 4 = 28 triangles in the given figure.

Find the number of triangles in the given figure.

The figure may be labelled as shown.
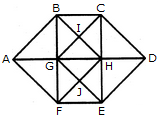
The simplest triangles are ABG, BIG, BIC, CIH, GIH, CDH, HED, GHJ, HJE, FEJ, GFJ and AGF i.e. 12 in number.
The triangles composed of two components each are ABF, CDE, GBC, BCH, GHG, BHG, GHF, GHE, HEF and GEF i.e. 10 in number.
The triangles composed of three components each are ABH, AFH, CDG and GDE i.e. 4 in number.
The triangles composed of four components each are BHF and CGE i.e. 2 in number.
Total number of triangles in the figure = 12 + 10 + 4 + 2 = 28.
