CBSE 11TH PHYSICS - Online Test
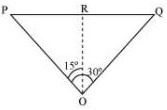
The positions of the observer and the aircraft are shown in the given figure.
Height of the aircraft from ground, OR = 3400 m
Angle subtended between the positions, ∠POQ = 30°
Time = 10 s
In ΔPRO:
tan 15° =
PR = OR tan 15°
=
ΔPRO is similar to ΔRQO.
∴PR = RQ
PQ = PR + RQ
= 2PR = 2 × 3400 tan 15°
= 6800 × 0.268 = 1822.4 m
∴ Speed of the aircraft =
= 182.24 m/s m/s
A 1.0-mol sample of an ideal gas is kept at 0.0C during an expansion from 3.0 L to 10.0 L. How much energy transfer by heat occurs with the surroundings in this process?
in isothermal process
hence
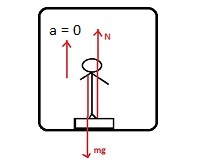
Mass of the man, m = 70 kg
Acceleration, a = 0
UsingNewton’s second law of motion,
wecan write the equation of motion as:
R – mg = ma
Where, ma is the net force acting on the man.
As the lift is moving at a uniform speed, acceleration a = 0
∴ R = mg = 70 × 10 = 700 N
∴ Reading on the weighing scale = 700 / g = 700 / 10 = 70 kg
Mass of the body, m= 0.5 kg
Velocity of the body
Initial velocity at x = 0 is u = 0
Final velocity at x = 2 m is
work done = Change in kinetic energy
angular momentum
A steel tape 1m long is correctly calibrated for a temperature of 27.0 C. The length of a steel rod measured by this tape is found to be 63.0 cm on a hot day when the temperature is 45.0 C. What is the actual length of the steel rod on that day? Coefficient of linear expansion of steel = 1.20
final length =63.0136cm