CBSE 11TH PHYSICS - Online Test
Q1. If the position- time graph is a straight line parallel to the time axis
Answer : Option B
Explaination / Solution:
Position-time graph of horizontal straight line parallel to time axis represents that the position of the body does not changes with the passage of time. So it represents the rest state of motion.
It means velocity of object is zero.
Q2. The speed of propagation of a sinusoidal wave is given by V=νλ where
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
No Explaination.
Q3. if particles A and B are moving with velocities and (each with respect to some common frame of reference, say ground.). Then, velocity of particle A relative to that of B is:
Answer : Option B
Explaination / Solution:
The relative velocity of an object A with respect to another object B is the velocity that object A would appear to have to an observer situated on object B moving along with it.
In simple words relative velocity of A with respect to Be is the vector difference between the velocities of A and B.
It is represented as
Q4. The potential energy of a spring whose spring constant is k and is compressed by x is
Answer : Option B
Explaination / Solution:
If a spring is stretched or compressed by a distance x from its natural length under the action of restoring force then
F = -kx
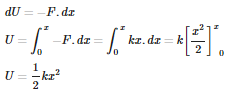
dU=−F.dx
Q5. Elastomers are materials
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
No Explaination.
Q6. In which type of process is the volume constant
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
An isochoric process is a thermodynamic process during which the volume of the closed system undergoing such a process remains constant.
Q7. Scientists strategy in general is to
Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
It is not practical to take into account all the complexities of a phenomenon in one go.
A good and scientific strategy is to focus first on the essential features, discover the basic principles and then introduce corrections to build a more refined theory of the phenomenon by removing its less significant aspects.
Q8. Friction is
Answer : Option B
Explaination / Solution:
Whenever a body of mass m moves or tends to move over the surface of another body, then the opposite force acts parallel to the surface contact which opposes the relative motion.
Q9. The radius of gyration of a body about an axis may be defined as the
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
It is the perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation to a point mass of mass m that gives an equivalent inertia to the original object (of mass, m)
if radius of gyration is k then
Q10. If a ball is spinning in an airflow it develops pressure difference between the lower and upper faces due differences in the
Answer : Option A
Explaination / Solution:
The Magnus effect is an observable phenomenon that is commonly associated with a spinning object that drags air faster around one side, creating a difference in pressure that moves it in the direction of the lower-pressure side.
The Magnus effect often occurs when a spinning sphere (or cylinder) curves away from its principal flight path.
This phenomenon is important in the study of the physics of many ball sports. It is also an important factor in the study of the effects of spinning on guided missiles—and has some engineering uses, for instance in the design of rotor ships and Flettner aeroplanes.
