CBSE 11TH PHYSICS - Online Test
Set of elements (vectors) in a vector space is called a basis, or a set of basis vectors, if the vectors are linearly independent and every vector in the vector space is a linear combination of this set.In more general terms, a basis is a linearly independent spanning set.
Given a basis of a vector space, every element of vector space can be expressed uniquely as a linear combination of basis vectors, whose coefficients are referred to as vector coordinates or components.
We can represent vector v as

This is Meyer's Equation
At constant volume as there is no work done on the gas(ΔV=0) all the heat supplied goes for the increase of internal energy. Hence temperature of body increases with less supply of heat. Whereas at constant pressure heat supplied accounts for both internal energy and work done on the gas.
if we increase temp. of 1 mole of gas by 1K or 1C then
This is also called Meyer's formula.
When a fluid is in motion, it must move in such a way that mass is conserved.Consider the steady flow of fluid through a duct (that is, the inlet and outlet flows do not vary with time). The inflow and outflow are one-dimensional, so that the velocity V and density are constant over the area A.
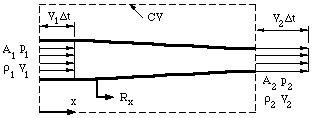
Now we apply the principle of mass conservation. Since there is no flow through the side walls of the duct, what mass comes in over goes out of , (the flow is steady so that there is no mass accumulation). Over a short time interval
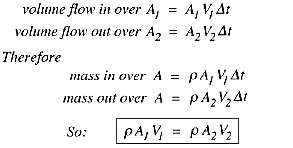
As volume is same so this equation can be written as
This is a statement of the principle of mass conservation for a steady, one-dimensional flow, with one inlet and one outlet. This equation is called the continuity equation for steady one-dimensional flow.
