CBSE 11TH PHYSICS - Online Test

Since force is a vector quantity, impulse is also a vector in the same direction.
Impulse J produced from time t1 to t2 is defined to be
where F is the resultant force applied from t1 to t2
force is related to momentum p by
F = dp/dt
therefore,
where is the change in linear momentum from time t1 to t2
The flow velocity u of a fluid is a vector field
which gives the velocity of an element of fluid at a position x and time t.
The flow of a fluid is said to be steady if u does not vary with time. That is if
Absolute error is defined as the magnitude of difference between the actual and the individual values of any quantity in question.
Say we measure any given quantity for n number of times and a1 , aa2 , aa3 ….. an are the individual values then Arithmetic mean
am =( [a1+a2+a3+ ….. + an]/n )
Now absolute error formula as per definition

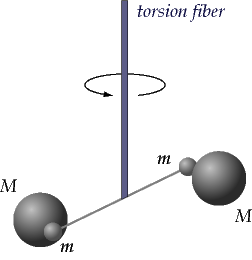
Cavendish's apparatus for experimentally determining the value of G involved a light, rigid rod about 2-feet long. Two small lead spheres were attached to the ends of the rod and the rod was suspended by a thin wire. When the rod becomes twisted, the torsion of the wire begins to exert a torsional force that is proportional to the angle of rotation of the rod. The more twist of the wire, the more the system pushes backwards to restore itself towards the original position.
