CBSE 11TH PHYSICS - Online Test
Average velocity is the displacement of an object, divided by the time it took to cover that distance.
Displacement is the straight line distance between the starting point and ending point of an object's motion.
Velocity is referred to as a vector quantity because it has both magnitude and direction.
angular displacement of particle about z axis
differentiate with respect to time
A null vector is a vector having magnitude equal to zero.It is represented by .
A null vector has no direction or it may have any direction.
Generally a null vector is either equal to resultant of two equal vectors acting in opposite directions or multiple vectors in different directions.
If Q is the energy supplied to the system U the change in internal energy, and W the work done on the environment, First Law of Thermodynamics states that
A resultant force causes acceleration and a change in the velocity of the body for as long as it acts.The change in momentum is equal to the product of the average force and duration. Conversely, a small force applied for a long time produces the same change in momentum, the same impulse, as a larger force applied for a short time interval.
Impulse J is
The impulse is the integral of the resultant force (F) with respect to time
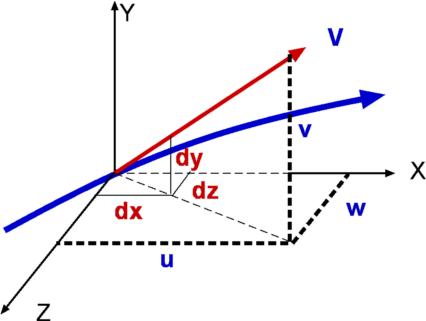
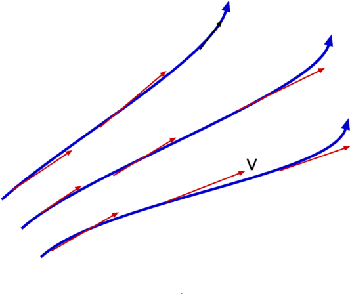
Streamlines are a family of curves that are instantaneously tangent to the velocity vector of the flow. These show the direction in which a massless fluid element will travel at any point in time
A streamline is one that drawn is tangential to the velocity vector at every point in the flow at a given instant and forms a powerful tool in understanding flows. This definition leads to the equation for streamlines.
where u,v, and w are the velocity components in x, y and z directions respectively as sketched.