CBSE 11TH CHEMISTRY - Online Test
Q1. One mole of a symmetrical alkene on ozonolysis, and subsequent treatment with ( Zn / H2 O ) gives two moles of an aldehyde having a molecular mass of 44 u.
The alkene is ---------.?
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
Ozonolysis of alkenes involves the addition of ozone molecule to alkene to form an unstable ozonide , and then cleavage of the ozonide by to smaller molecules .
2- butene is a symmetrical alkene , which on ozonolysis yields two moles of having molecular mass of 44 u. as per reaction given below,
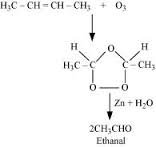
Q2. The typical range of molar enthalpies for the strongest intermolecular (Hydrogen) bonds is
Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
A hydrogen bond is the electrostatic attraction between two polar groups that occurs when a hydrogen (H) atom linked to a small sized highly electronegative atom such as nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), or fluorine (F). Therefore unlike a covalent bond, it has very low dissociation energy with a range of molar enthalpy =
( 4 − 25 ) kJ
Q3. Deforestation is responsible for:
Answer : Option B
Explaination / Solution:
Deforestation is responsible for desertification
Q4. Lines in the hydrogen spectrum which appear in the visible region of the electromagnetic Spectrum, then they are called as
Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
The Balmer series or Balmer lines in atomic physics, is the designation of one of a set of six named series describing the spectral line emissions of the hydrogen atom. The Balmer series is calculated using the Balmer formula, an empirical equation discovered by Johann Balmer in 1885 Balmar series lies in visible region of Electromagnetic spectrum.
Q5. Syngas is mixture of
Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
Synthesis gas or briefly, syngas, is a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen. Syngas can be produced from many sources, including natural gas, coal, biomass, or virtually any hydrocarbon feedstock, by reaction with steam or oxygen. Syngas is a crucial intermediate resource for production of hydrogen, ammonia, methanol, and synthetic hydrocarbon fuels
Q6. Calculate the heat and the work associated with a process in which 5.00 mol of gas expands reversibly at constant temperature T = 298 K from a pressure of 10.00 to 1.00 atm
Answer : Option B
Explaination / Solution:
for isothermal process ΔU=0 while –w=nRTln(P1/P2) = q
Q7.
Based on VSEPR theory, the number of 90 degree F — Br — F angles in is
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
Steric no. of BrF5 is 6 so geometry is octahedral. It will have 5 bps and one lp which is present on axial position. Because of distortion caused by lp there is no 90o F—Br—F bond angle in BrF5 .
Q8. Heating a pulverised mixture of limestone and clay in a rotary kiln is used in the manufacture of:
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
Heating a pulverised mixture of limestone and clay in a rotary kiln is used in the manufacture of Portland cement
Q9. Covalent bond can undergo fission in two different ways. The correct representation involving a heterolytic fission of is


Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
arrows are shown in the direction of movement of electrons.
Q10. The vapor pressure of different substances at the same temperature increases if
Answer : Option A
Explaination / Solution:
if the intermolecular forces of the substance are weak then vapour pressure increases.
