CBSE 11TH CHEMISTRY - Online Test
Using the standard electrode potential of redox couples given below find out which of the following is the strongest oxidising agent.
E0 values: Fe3+/Fe2+ = +0.77; I2/I-(s) = +0.54; Cu2+/Cu = +0.34; Ag+/Ag = +0.80
Choose the most appropriate option to complete the statement -
" Whenever there is a rearrangement of atoms which makes or breaks chemical bonds ------------------------ "
2- Methyl -2 - pentene when treated with ozone forms an unstable ozonide intermediate . The ozonide when treated with yields an aldehyde (propionaldehyde ) and a ketone ( acetone ) as the final products The conversion reactions are represented as below.
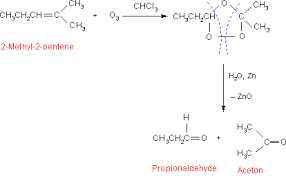
Thus , the compound A is (2-Methyl -2 -pentene )
The bond lengths depend upon the number and type of bonds present in a molecule . Greater the number of bonds shorter would be the bond length.
Thus , the given molecules are all diatomic molecules where ,
(i) has the smallest bond length as it is triple bonded.
(ii) is double bonded so its bond length is greater than .
(iii) both , though single bonded , the bond length of is greater than that of due to its larger atomic size.
Hence , the correct increasing order of given molecules is
Find energy of the photons which correspond to light of frequency Hz (Hint: h = Planck’s constant = 6.626 × Js)
We know Planck's equation is
where E is energy, h is Planck’s constant, and is frequency.
Put given values,
E =
There are three isotopes of hydrogen namely, protium 1H1, deuterium 1H2 or D and lastly tritium 1H3 or T.
Out of these three isotopes of hydrogen, only tritium is radioactive in nature which emits low energy b particles. As the electronic configuration of isotopes is same, they all have similar chemical properties. But they have a difference in their rates of reaction, this happens because of the different bond disassociation enthalpies.
