CBSE 11TH CHEMISTRY - Online Test
Q1. spin quantum number with two spin states of the electron represented by two arrows, ↑ (spin up) and ↓ (spin down) was introduced to account for
Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
In 1920, Otto Stern and Walter Gerlach designed an experiment, which unintentionally led to the discovery that electrons have their own individual, continuous spin even as they move along their orbital of an atom. The experiment mentioned above by Otto Stern and Walter Gerlach was done with silver which was put in an oven and vaporized. The result was that silver atoms formed a beam that passed through a magnetic field in which it split in two.
Q2. Ozone hole is :
Answer : Option A
Explaination / Solution:
Ozone hole is the depletion of ozone layer in the stratosphere caused by some pollutants that react with ozone to convert it into other form, decreasing the thickness of the ozone layer there which is called as the "hole".
Q3. Molarity is defined as,
Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
Molarity is the most widely used method of expressing the strength or concentration of a solution .
It is denoted by ' M ' .
Molarity is defined as number of . of moles of solute present per litre of solution.
Mathematically ,
Molarity ( M )
= Number of moles of solute / Volume of solution in Litres
Q4. Presence of extensive hydrogen bonding between water molecules is responsible for
Answer : Option A
Explaination / Solution:
hydrogen bonding is responsible for liquid and solid states.
Q5. In NO-3 ion, the number of bond pairs and lone pairs of electrons on nitrogen atom are
Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
The nitrate ion is formed by the loss of the hydrogen ion, and so its structure is:
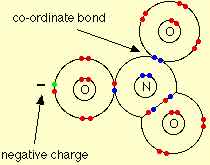
Around the central nitrogen there are 4 pairs of shared electrons, and no remaining lone pair. The original lone pair has now become a bonding pair. Two of those pairs make up a double bond. The double bond unit and the two single bonds arrange themselves as far apart as possible in a trigonal planar arrangement - exactly the same as the carbonate ion.
Q6. What is the type of hybridisation of each carbon in the compound
Answer : Option B
Explaination / Solution:
C in CH3 is and C of C=O bond is .
Q7.
What is M?
Answer : Option B
Explaination / Solution:
M is alkali metal. Alkali metals reacts with water vigorously to form hydroxide (OH-) and dihydrogen (H2)
Q8. behaviour of the gas becomes more ideal when
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
This question is based on understanding the concept of molecular interactions between molecule of real gases which is least at low P and High T condition. Thus under these conditions real gases behave as ideal.
Q9. The value of for a reaction is directly related to the thermodynamics of the reaction and in particular,
Answer : Option A
Explaination / Solution:
Δ G = -RTlnK
Q10. Majority of the reactions of alkynes are the examples of
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
Alkynes have two pi bonds,hence they are electron rich species.They attract electrophiles thereby undergoing electrophilic addition reactions.
