Fluid Mechanics and Thermal Sciences - Online Test
Q1. A pump handling a liquid raises its pressure from 1 bar to 30 bar. Take the
density of the liquid as 990 kg /m3. The isentropic specific work done by the
pump in kJ/kg is
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
Work done by the pump = 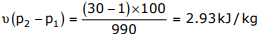
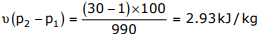
Q2. A spherical steel ball of 12mm diameter is initially at 1000K. It is slowly cooled in
a surrounding of 300K. The heat transfer coefficient between the steel ball and
the surrounding is 5W /m2 K . The thermal conductivity of steel is 20W /mK . The
temperature difference between the centre and the surface of the steel ball is
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
Bi = hL/K = 5 ×0.002/20 = 0.0005
For the given condition the Biot number tends to zero, that means conduction
resistance is far less than convection resistance. Therefore temperature between
the centre and surface is very small.
Q3. An ideal Brayton cycle, operating between the pressure limits of 1 bar and 6 bar,
has minimum and maximum temperatures of 300K and 1500K. The ratio of
specific heats of the working fluid is 1.4. The approximate final temperatures in
Kelvin at the end of the compression and expansion processes are respectively
Answer : Option A
Explaination / Solution:
Ideal Brayton cycle
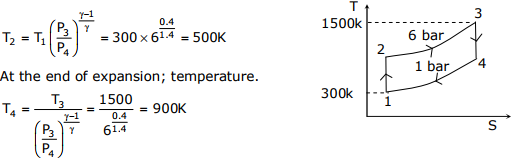
At the end of compression, temperature.
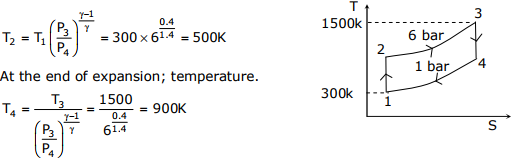
Q4. In an experimental set-up, air flows between two stations P and Q adiabatically.
The direction of flow depends on the pressure and temperature conditions
maintained at P and Q. The conditions at station P are 150kPa and 350K. The
temperature at station Q is 300K.
The following are the properties and relations pertaining to air:
Specific heat at constant pressure, Cp = 1.005kJ / kgK;
Specific heat at constant volume, Cv = 0.718kJ / kgK;
Characteristic gas constant, R = 0.287kJ / kgK
Enthalpy, h = CpT
Internal energy, u = CvT
If the air has to flow from station P to station Q, the maximum possible value of
pressure in kPa at station Q is close to
Answer : Option B
Explaination / Solution:
To cause the flow from P to Q, change in entropy (SP - SQ) should be
greater than zero 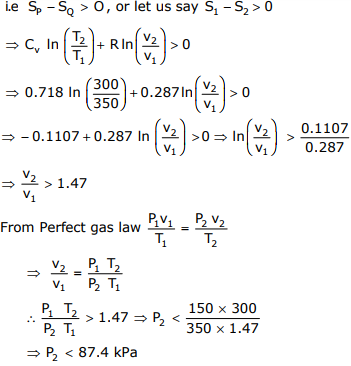
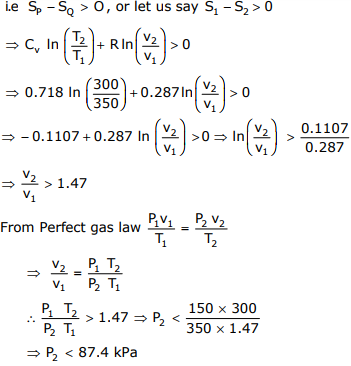
∴ The maximum value of pressure at Q = 87 kPa
Q5. In an experimental set-up, air flows between two stations P and Q adiabatically. The direction of flow depends on the pressure and temperature conditions maintained at P and Q. The conditions at station P are 150kPa and 350K. The temperature at station Q is 300K.
The following are the properties and relations pertaining to air:
Specific heat at constant pressure, Cp = 1.005kJ / kgK;
Specific heat at constant volume, Cv = 0.718kJ / kgK;
Characteristic gas constant, R = 0.287kJ / kgK
Enthalpy, h = CpT
Internal energy, u = CvT
If the pressure at station Q is 50kPa, the change in entropy (SQ - SP) in kJ/kgK is
Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
No Explaination.
Q6. The temperature and pressure of air in a large reservoir are 400K and 3 bar
respectively. A converging–diverging nozzle of exit area 0.005m2 is fitted to the
wall of the reservoir as shown in the figure. The static pressure of air at the exit
section for isentropic flow through the nozzle is 50kPa. The characteristic gas
constant and the ratio of specific heats of air are 0.287kJ/kgK and 1.4
respectively

The density of air in kg/ m3 at the nozzle exit is
Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
Given data:
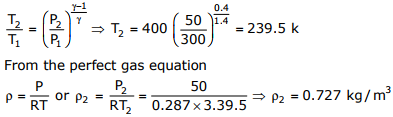
T1 = 400k, P1 = 300 kPa, P2 = 50kPa, R = 0.289kJ / kgK
v = 1.4, A2 = 0.005m2
The happened process from entrance to exit is isentropic process, therefore
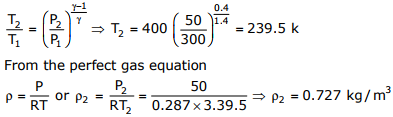
Q7. The temperature and pressure of air in a large reservoir are 400K and 3 bar respectively. A converging–diverging nozzle of exit area 0.005m2 is fitted to the wall of the reservoir as shown in the figure. The static pressure of air at the exit section for isentropic flow through the nozzle is 50kPa. The characteristic gas constant and the ratio of specific heats of air are 0.287kJ/kgK and 1.4 respectively


The mass flow rate of air through the nozzle in kg/s is
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
No Explaination.
Q8. A mass m of a perfect gas at pressure p1 and volume V1 undergoes an isothermal process. The
final pressure is p2 and volume is V2. The work done on the system is considered positive. If R
is the gas constant and T is the temperature, then the work done in the process is
Answer : Option B
Explaination / Solution:
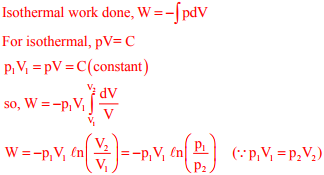
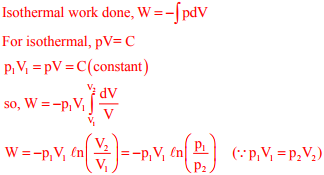
Q9. The emissive power of a blackbody is P. If its absolute temperature is doubled, the emissive
power becomes.
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
No Explaination.
Q10. Which one of the following statement is TRUE?
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
No Explaination.
