Logical Reasoning - Online Test

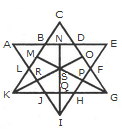
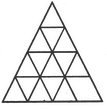
The simplest triangles are ABL, BCD, DEF, FGP, PGH, QHI, JQI, KRJ and LRK i.e. 9 in number.
The triangles composed of two components each are OSG, SGQ, SPI, SRI, KSQ, KMS, FGH, JHI and JKL i.e. 9 in number.
There is only one triangle i.e. KSG which is composed of four components.
The triangles composed of five components each are NEI, ANI, MCG and KCO i.e. 4 in number.
The triangles composed of six components each are GMK and KOG i.e. 2 in number.
There is only one triangle i.e. AEI composed of ten components.
There is only one triangle i.e. KCG composed of eleven components.
Therefore, Total number of triangles in the given figure = 9 + 9+1 + 4 + 2+1 + 1 = 27.
A). The prices of liquor are lower in rural areas than in urban areas.
B). Percentage of people consuming liquor is more in rural areas than in urban areas.
C). There are many unauthorized spurious liquor shops in the rural areas.
D). Number of people suffering from food poisoning due to consumption of liquor as a percentage of people who consume liquor is almost equal for both urban areas and rural areas.
Which of the above statements numbered (A), (B), (C) and (D) if true will most weaken the given argument?
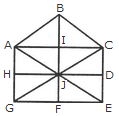
The simplest triangles are ABI, BIC, AIJ, CIJ, AHJ, CDJ, JHG, JDE, GJF and EJF i.e. 10 in number.
The triangles composed of two components each are ABC, BCJ, ACJ, BAJ, AJG, CJE and GJE i.e. 7 in number.
The triangles composed of four components each are ACG, ACE, CGE and AGE i.e. 4 in number.
Total number of triangles in the figure =10+ 7 + 4 = 21.

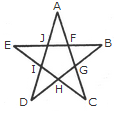
The simplest triangles are AJF, FBG, GCH, HDI and IEJ i.e. 5 in number.
The triangles composed of three components each EBH, AIC, EFC, ADG and BJD i.e. 5 in number.
Thus, there are 5 + 5 = 10 triangles in the figure.
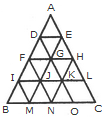
The horizontal lines are DE, FH, IL and BC i.e. 4 in number.
The slanting lines are AC, DO, FN, IM, AB, EM and HN i.e. 7 in number.
Thus, there are 4 + 7 = 11 straight lines in the figure.
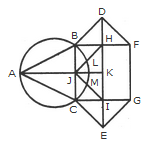
The simplest triangles are ABJ, ACJ, BDH, DHF, CIE and GIE i.e. 6 in number.
The triangles composed of two components each are ABC, BDF, CEG, BHJ, JHK, JKI and CJI i.e. 7 in number.
There is only one triangle JHI which is composed of four components.
Thus, there are 6 + 7 + 1 = 14 triangles in the given figure.
