CBSE 12TH BIOLOGY - Online Test
Q1. DNA sequence that code for protein are known as
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
Exons are coding sections of an RNA transcript, or the DNA encoding it, that are translated into protein. Exons can be separated by intervening sections of DNA that do not code for proteins, known as introns.
Q2. The “hidden hunger” is due to
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
If a person get food that do not contain all micronutrient, protein and vitamins in required amount as per age, sex, working condition, this condition is called hidden hunger.
Q3. Conserving biodiversity provides major contribution to economy as :
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
Ecotourism is a form of tourism involving visiting fragile, pristine, and relatively undisturbed natural areas, intended as a low-impact and often small scale alternative to standard commercial mass tourism.
Conserving biodiversity provides a number of benefits along with contributaion to economy of the country by ecotourism. Large number of foreigner visit to diversity rich countries as tourist.
Q4. The release of sperms from Sertoli cells into the cavity of seminiferous tubules is called as
Answer : Option C
Explaination / Solution:
Spermiation is the process of release of sperms from Sertoli cells into the cavity of seminiferous tubules.
Q5. In human beings, if ovum fertilizes with a sperm carrying X-chromosome the zygote develops into
Answer : Option B
Explaination / Solution:
Male produce two kinds of sperms, half carrying X and half carrying Y sex chromosome besides 22 autosomes. If ovum is fertilized by sperm carrying X chromosome the sex of child developed is female.
Q6. A symbiotic relationship/interaction in which 'one species benefits and the other species is not affected' is called
Answer : Option B
Explaination / Solution:
Commensalism is a relationship between two organisms where one receives a benefit or benefits from the other and the other is not affected by it. In other words, one is benefited and the other is neither benefited nor harmed.
Example:
- Orchids - Some orchids grow on trees and that does not harm the tree.
- Pilot fish - Pilot fish live around sharks, sea turtles and rays and eat the parasites that live on them as well as leftover food they do not eat. Young pilot fish gather around jellyfish and seaweeds.
Q7. The gases which are transparent to solar radiation but retain long wave heat radiations are called
Answer : Option A
Explaination / Solution:
A greenhouse gas (often abbreviated as GHG) is a gas that both absorbs and emits radiation in the infrared range, commonly called thermal radiation or heat. When present in the atmosphere, these gases trap radiation in the form of heat, causing a warming process called the greenhouse effect.
These gases are transparent to solar radiation.
Q8. Nucleosome is seen in
Answer : Option D
Explaination / Solution:
The nucleosome is the fundamental subunit of chromatin. Nucleosome is clearly seen in fungus called Yeast.
Q9. Praying mantis is a good example of
Answer : Option A
Explaination / Solution:
The Praying Mantis is a large insect from the order of Mantodea. It's called the "Praying" Mantis because it often stands in a pose that looks like it is praying.
Many animals have evolved to exhibit some form of camouflage, which is an adaptation that allows animals to blend in with certain aspects of their environment
Praying Mantids use camouflage to hide from predators and sneak up on prey. Different species vary in color from dark brown to green. These colors allow them to blend into their natural surroundings such as tree bark or green plant leaves.
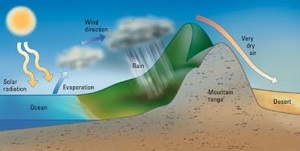
Q10. In a rain shadow area biome is represented by
Answer : Option A
Explaination / Solution:
A rain shadow is a dry area on the leeward side of a mountainous area (away from the wind). The mountains block the passage of rain-producing weather systems and cast a "shadow" of dryness behind them. Wind and moist air is drawn by the prevailing winds towards the top of the mountains, where it condenses and precipitates before it crosses the top. The air, without much moisture left, advances behind the mountains creating a drier side called the "rain shadow".