CBSE 11TH PHYSICS - Online Test
Mean is the average of all numbers. So mean of all the absolute errors will be given by
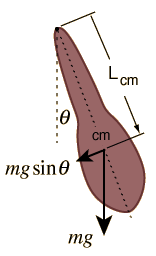
Torque;,a= angular accleration
so Time period T is :
T = 2π
The value of G was experimentally determined by Lord Henry Cavendish using a torsion balance.Cavendish brought two large lead spheres near the smaller spheres attached to the rod. Since all masses attract, the large spheres exerted a gravitational force upon the smaller spheres and twisted the rod a measurable amount. Once the torsional force balanced the gravitational force, the rod and spheres came to rest and Cavendish was able to determine the gravitational force of attraction between the masses.Cavendish expressed his result in terms of the density of the Earth.
After converting to SI units, Cavendish's value for the Earth's density, 5.448 g cm−3, gives
- G = 6.74×10−11 m3 kg–1 s−2
Today, the currently accepted value is 6.67259 x 10-11 N m2/kg2.
Instantaneous velocity is the velocity of an object in motion at a specific point in time. This is determined similarly to average velocity, but we narrow the period of time so that it approaches zero.
The formula for instantaneous velocity is the limit as t approaches zero of the change in position over the change in t.
Mathematically,
Where x is the given function with respect to time t. The Instantaneous Velocity is expressed in m/s.
In the equation
y(x, t) = a sin (kx + t + )
the term with distance travelled 'x' is called angular wave number or propagation constant
Hence k is the angular wave number.
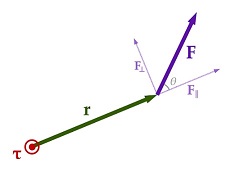
Torque = Force x Perpendicular distance of the line of action of the force from the axis of rotation. It is also called moment of force.
torque is defined as the cross product of the vector by which the force's application point is offset relative to the fixed suspension point (distance vector) and the force vector, which tends to produce rotational motion.
A unit vector in a normed vector space is a vector (often a spatial vector) of length 1. A unit vector is often denoted by a lowercase letter with a circumflex, or "hat": (pronounced "i-hat"). The term direction vector is used to describe a unit vector being used to represent spatial direction.
a unit vector directed along the positive x axis
= a unit vector directed along the positive y axis
= a unit vector directed along the positive z axis
