CBSE 11TH PHYSICS - Online Test
Using the assumption of little spheres (for interatomic space) the spacing between the molecules at about 2X10-10 m i.e.
The size of an atom is about an angstrom (10 -10 m) . In solids, which are tightly packed, atoms are spaced about a few angstroms (2 Å) apart.
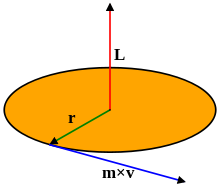
The motion of a particle under a central force F always remains in the plane defined by its initial position and velocity.This may be seen by symmetry. Since the position r, velocity v and force F all lie in the same plane, there is never an acceleration perpendicular to that plane, because that would break the symmetry between "above" the plane and "below" the plane.
To demonstrate this mathematically, it suffices to show that the angular momentum of the particle is constant. This angular momentum L is defined by the equation
Displacement is defined to be the change in position of an object. It can be defined mathematically with the following equation:
refers to the value of the final position.
refers to the value of the initial position.
is the symbol used to represent displacement.
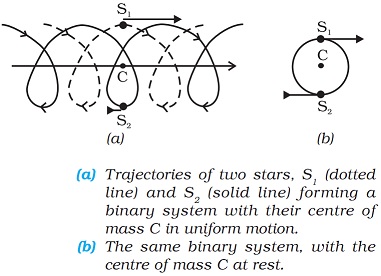
A double star or visual double is a pair of stars that appear close to each other in the sky as seen from Earth when viewed through an optical telescope.
In absence of external force Centre of mass of double star moves like a free particle. In Centre of mass frame both stars moving in a circle about the Centre of mass which is at rest and both star are diametrically opposite to each other.
Thus in our frame of reference, the trajectories of the stars are a combination of (i) uniform motion in a straight line of the Centre of mass and (ii) circular orbits of the stars about the Centre of mass.
Work done = force in the direction of displacement multiplied by displacement
Triangle law of vector addition states that when two vectors are represented by two sides of a triangle in magnitude and direction taken in same order then third side of that triangle represents in magnitude and direction the resultant of the vectors.

Taken in same order mean tail of Vector B must coincide with head of vector A as shown in image.
